
[ad_1]
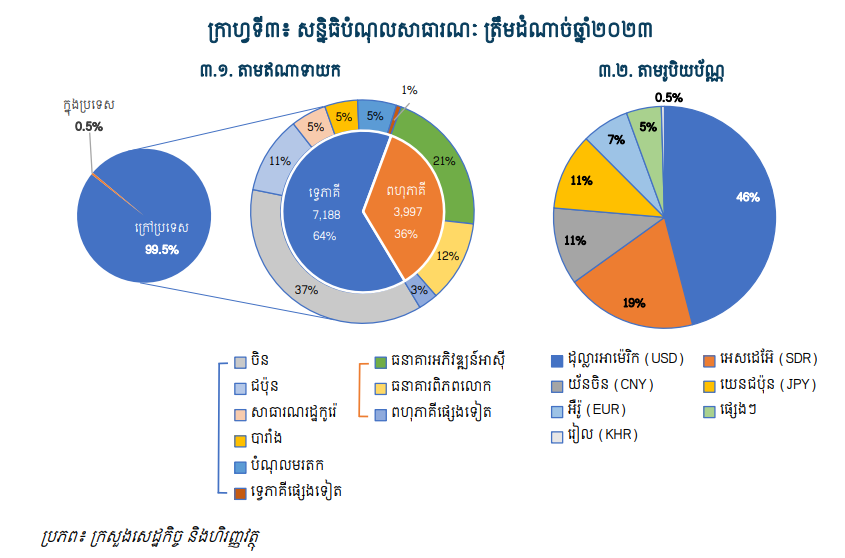
By the end of 2023, Cambodia’s total public debt stock will be approximately $11.238 billion The bulk of this is mainly foreign public debt, about $11.185 billion This is equivalent to 99.5% of the total stock. This is in accordance with the Public Debt Management Strategy Paper (2024-2028) recently released by the Royal Government. Bilateral frameworks account for about 64% and multilateral frameworks account for about 36%.

In the bilateral framework, China accounts for 37%, Japan accounts for 11%, South Korea accounts for 5%, France accounts for 5%, and legacy debt accounts for 6%. As for multilateral debt, ADB accounts for 21%, the World Bank accounts for 12%, and other multilateral debt accounts for 3%.
The Public Debt Management Strategy Paper 2024-2028 confirms that the Royal Government of Cambodia has set a public debt ceiling for borrowing from financial institutions and foreign development partners in the current economic environment. 1.7 to 2 billion SDA per year or approximately ($2.3 to 2.7 billion) If necessary, it can be increased to 2.5 billion SDA per year, but not more than 10 billion SDA (or$13.5 billion) within 5 years.
To support the implementation of the first phase of the Pentagon strategy, the Royal Government has decided to implement Public Debt Management Strategy 2024-2028 In the global, regional and Cambodian context, and with a high degree of caution and flexibility, five key principles include:
1) Borrowing loans reasonably within the scope of financial and economic conditions
2) Borrowing loans at preferential levels or on preferential terms
3) Borrow only to priority sectors that support sustainable economic growth and sectors that increase economic productivity or productivity.
4) Use credit in a transparent, accountable, efficient and effective manner
5) In accordance with the principles of public investment management, credit financing must be used for high-standard and high-quality public infrastructure investment projects that meet the country’s development needs in the new stage, especially to ensure the realization of economic, social, environmental and climate change capabilities.

In the two decades before the Kovid-19 crisis, Cambodia’s economic growth averaged more than 7% per year, leading toCambodia joins the ranks of lower-middle-income countries in 2015 People’s living standards have improved significantly GDP per capita increases more than fivefold, from $464 in 2004 to about $2,520 in 2023 While the poverty rate has continued to decline steadily, from over 54% in 2004 to 13.5% in 2014, it was estimated to be below 10% before the Covid-19 crisis.
Through past efforts, Cambodia has established a strong public debt management system that combines many key components, including clear legal frameworks and procedures, adequate institutional and human resource capacity, information technology systems for management operations and storage of comprehensive data, and in particular, the establishment and maintenance of a public debt management system. The main disciplinary principles and management strategies have been strictly implemented three times since 1993, the first from 2011 to 2018, the second from 2015 to 2018, and the third from 2019 to 2023.
By implementing three public debt management strategies, Cambodia’s public debt situation has been managed in an orderly and efficient manner, with the ability to maintain “sustainability” and “low risk”. The current foreign public debt price index to GDP ratio averages only around 18% between 2019 and 2023, compared with a benchmark ratio of 40%.។
At the same time, the Royal Government has begun to raise funds from the domestic market through the issuance of national securities, which is the first new source of financing in 2022, and will continue to actively implement all measures and action plans stipulated in the 2022 Government Budget and the 2023-2028 Securities Development Policy Framework to establish a strong and comprehensive national securities issuance and trading management system.
[ad_2]
Source link


